Ln: Difference between revisions
(Marked this version for translation) |
(updates from Blockument) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> | <languages/> | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<section begin="image"/>[[File:ln.png|alt=The Natural Log Block|thumb]]<section end="image"/> | |||
==Usage== | |||
<!--T:2--> | <!--T:2--> | ||
<p id="tooltip">Returns the natural log of the input.</p> | <p id="tooltip">Returns the natural log of the input.</p> | ||
==Syntax== | |||
Inputs in this block: | |||
#a number | |||
==Example== | |||
[[File:ln_example.gif|alt=Ln example gif|thumb]] | |||
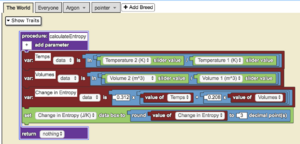
[[File:ln_example.png|alt=Ln example code|thumb]] | |||
This models the change in entropy for the gas, Argon (Ar). The initial and final states are configurable via sliders that the user can manipulate. The calculation for the change in entropy is continuous, meaning that as the slider values are changed, the entropy calculation will run automatically. The equation to calculate the change in entropy uses the ln function which is employed above. | |||
<!--T:1--> | <!--T:1--> | ||
Revision as of 16:45, 14 August 2023
Usage
Returns the natural log of the input.
Syntax
Inputs in this block:
- a number
Example
This models the change in entropy for the gas, Argon (Ar). The initial and final states are configurable via sliders that the user can manipulate. The calculation for the change in entropy is continuous, meaning that as the slider values are changed, the entropy calculation will run automatically. The equation to calculate the change in entropy uses the ln function which is employed above.