Data Box/en: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[File:data_box_example.gif|alt=Data Box example gif|thumb]] | [[File:data_box_example.gif|alt=Data Box example gif|thumb]] | ||
[[File: | [[File:quotient_example.png|alt=Data Box example code|thumb]] | ||
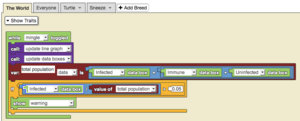
This is a model of an epidemic. To monitor the spread of the epidemic, data boxes and a line graph have been employed to monitor immune, uninfected, and infected populations. An epidemic occurs when the infected population exceeds the expected infected population. Thus, when over 5% of the population is infected, the warning label is shown. | This is a model of an epidemic. To monitor the spread of the epidemic, data boxes and a line graph have been employed to monitor immune, uninfected, and infected populations. An epidemic occurs when the infected population exceeds the expected infected population. Thus, when over 5% of the population is infected, the warning label is shown. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:53, 16 August 2023
Returns the value of a selected data box.
[▼] data box is a code block from the Interface drawer.
Usage
[▼] data box refers to the value of a selected data box.
Note: You should use data boxes for numerical values and labels for textual values. One advantage of using a data box is that you can title it.
Syntax
Input:
- a data box from the dropdown menu
Example
This is a model of an epidemic. To monitor the spread of the epidemic, data boxes and a line graph have been employed to monitor immune, uninfected, and infected populations. An epidemic occurs when the infected population exceeds the expected infected population. Thus, when over 5% of the population is infected, the warning label is shown.