Not Equals/es: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "No Igualar") |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> | <languages/> | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
<section begin="image"/>[[File:not_equals.png|alt=The Not Equals Block|thumb]]<section end="image"/> | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
==Usage== | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
<p id="tooltip">Determines whether the two inputs are unequal and returns true or false.</p> | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
==Syntax== | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
Inputs in this block: | |||
#a number | |||
#a number | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
==Example== | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
[[File:not_equals_example.gif|alt=Not Equals example gif|thumb]] | |||
[[File:not_equals_example.png|alt=Not Equals example code|thumb]] | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
The model above is of a debilitating disease. Agents that do not have the disease, as determined by an [[Special:MyLanguage/If|if]] statement (‘if my color != color red’), are able to move normally. While the diseased agents are only able to move at a tenth of their usual speed. The result is a disease that spreads much more slowly, as diseased agents cannot move quickly into groups of healthy agents to infect them. | |||
</div> | |||
[[Category:Lógica]] | [[Category:Lógica]] | ||
[[Category:Code Block]] | [[Category:Code Block]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:37, 14 August 2023
Usage
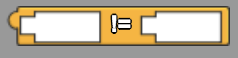
Determines whether the two inputs are unequal and returns true or false.
Syntax
Inputs in this block:
- a number
- a number
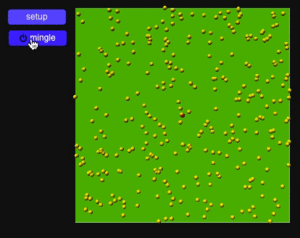
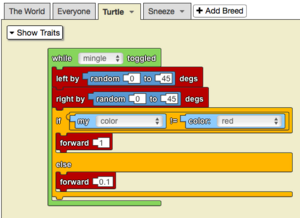
Example
The model above is of a debilitating disease. Agents that do not have the disease, as determined by an if statement (‘if my color != color red’), are able to move normally. While the diseased agents are only able to move at a tenth of their usual speed. The result is a disease that spreads much more slowly, as diseased agents cannot move quickly into groups of healthy agents to infect them.